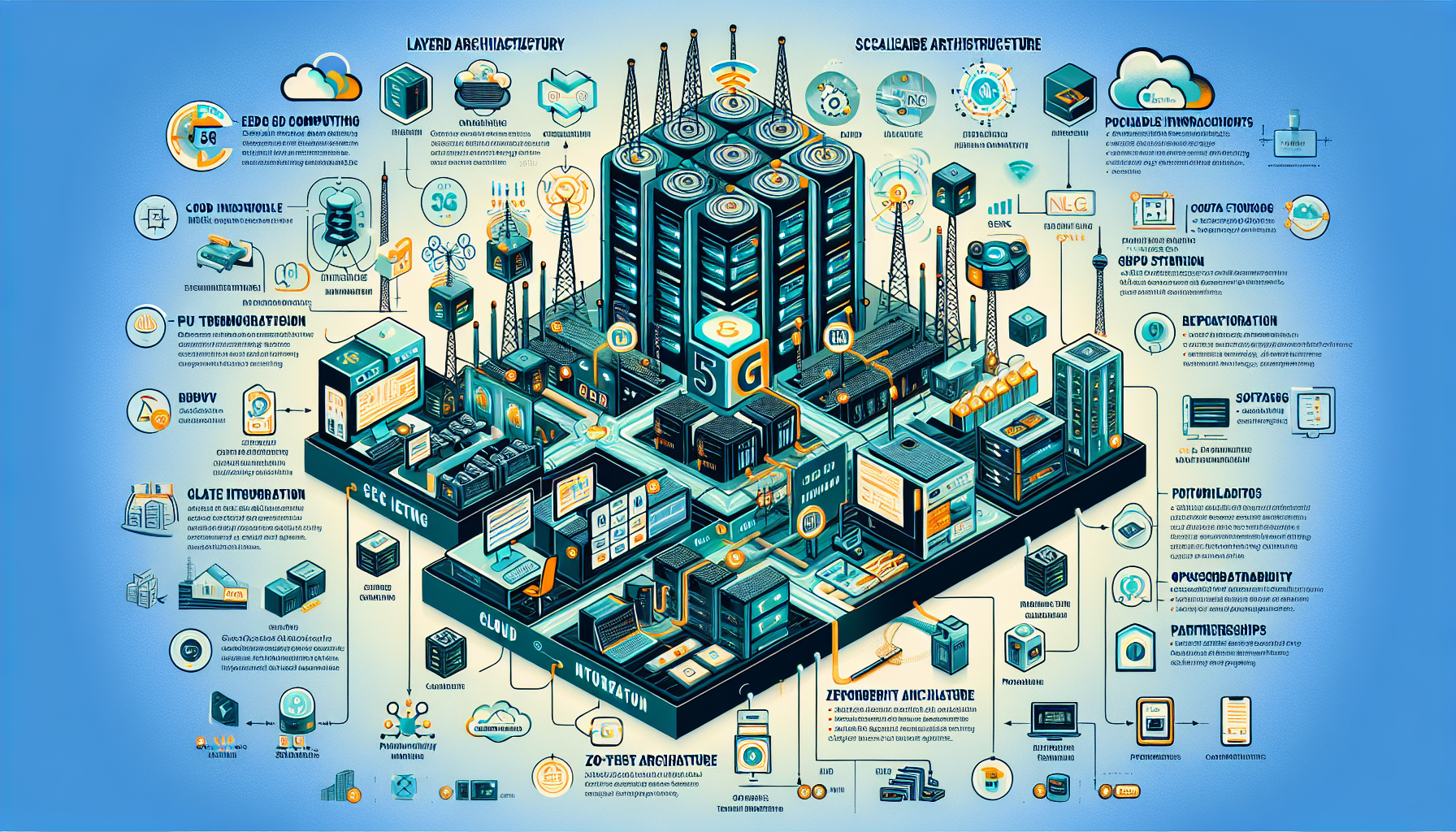
Implementing IT infrastructure for 5G networks requires a combination of robust hardware, advanced software, and scalable architecture to support the high-speed, low-latency, and massive connectivity demands of 5G technology. Here’s a step-by-step approach tailored for an IT manager overseeing datacenters, storage, servers, virtualization, and related technologies:
1. Design the Infrastructure Architecture
- Edge Computing: Deploy edge datacenters close to end-users to reduce latency and improve performance. 5G networks benefit from processing data locally rather than sending it to centralized datacenters.
- Cloud Integration: Integrate with hybrid or multi-cloud environments to ensure scalability and flexibility.
- Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs): Implement NFV (Network Function Virtualization) to replace hardware-based network appliances with virtualized software running on commodity hardware.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Use SDN to enable dynamic configuration and scalability of network resources.
2. Build Scalable Datacenters
- Hardware Considerations:
- Deploy high-density servers with multi-core CPUs and high-speed memory to handle 5G workloads.
- Incorporate GPU cards (e.g., NVIDIA or AMD) for AI and real-time data processing at scale.
-
Use NVMe-based storage for ultra-high-speed data reads/writes.
-
Cooling Systems:
-
5G workloads generate significant heat. Implement advanced cooling solutions, such as liquid cooling systems, especially for edge datacenters.
-
Redundancy and Reliability:
- Ensure high availability and redundancy for mission-critical systems.
- Implement failover clustering and disaster recovery plans.
3. Optimize Storage Systems
- High-Speed Storage:
- Use NVMe drives or all-flash storage solutions to support the rapid data exchanges required by 5G applications.
-
Implement scalable storage systems that can accommodate the massive volumes of data generated by IoT devices and 5G applications.
-
Data Tiering:
-
Use tiered storage (hot, warm, cold) to optimize cost and performance.
-
Backup Solutions:
- Implement automated backup solutions with deduplication to ensure data integrity and quick recovery.
- Consider object storage for archiving and long-term data retention.
4. Enable Virtualization and Kubernetes
- Containerization:
- Deploy Kubernetes clusters to manage containerized applications for microservices architecture. This is essential for 5G use cases like IoT, AR/VR, and video streaming.
-
Leverage GPU-enabled Kubernetes nodes for workloads requiring AI/ML or high-performance computing.
-
Virtual Machines:
- Use hypervisors such as VMware, Hyper-V, or KVM for virtualized environments.
- Implement orchestration tools like OpenStack for managing large-scale virtualized infrastructure.
5. AI and Automation
- AI for Network Optimization:
- Deploy AI models to optimize traffic routing, predict failures, and improve network efficiency.
-
Use AI-driven analytics for real-time monitoring and decision-making.
-
Automation Tools:
- Implement infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tools like Terraform or Ansible for automated provisioning and configuration.
- Use automation platforms for continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
6. Networking
- 5G Core Network Infrastructure:
- Deploy 5G core components (e.g., AMF, SMF, UPF) in a virtualized or containerized environment.
-
Use SDN to dynamically configure and manage network traffic.
-
High-Capacity Connectivity:
- Upgrade to high-speed, low-latency switches and routers (e.g., 100Gbps or 400Gbps Ethernet).
- Implement redundant network paths to ensure reliability.
7. Security
- Zero Trust Architecture:
- Implement zero-trust security principles across the infrastructure, requiring verification for every user and device.
- Encryption:
- Use encryption (TLS/SSL, IPSec) for data in transit and at rest.
- DDoS Protection:
- Deploy DDoS mitigation tools to protect against volumetric attacks on 5G networks.
8. Monitoring and Management
- Observability Tools:
- Implement tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack to monitor server performance, network traffic, and application health.
- Network Performance Monitoring (NPM):
- Use advanced NPM tools to measure latency, jitter, and packet loss in real-time.
- Capacity Planning:
- Continuously monitor resource utilization to scale storage, compute, and network capacity based on demand.
9. Compliance and Standards
- 5G Standards:
- Ensure compatibility with 3GPP standards for 5G architecture and operations.
- Data Privacy Regulations:
- Comply with data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) to protect sensitive customer data.
10. Collaboration with Telecom Providers
- Partner with telecom providers and 5G equipment vendors (e.g., Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei) for seamless integration of IT infrastructure with the 5G network.
By designing an infrastructure that is scalable, secure, and optimized for low-latency and high-throughput demands, you can create a 5G-ready environment to support next-generation applications and services.