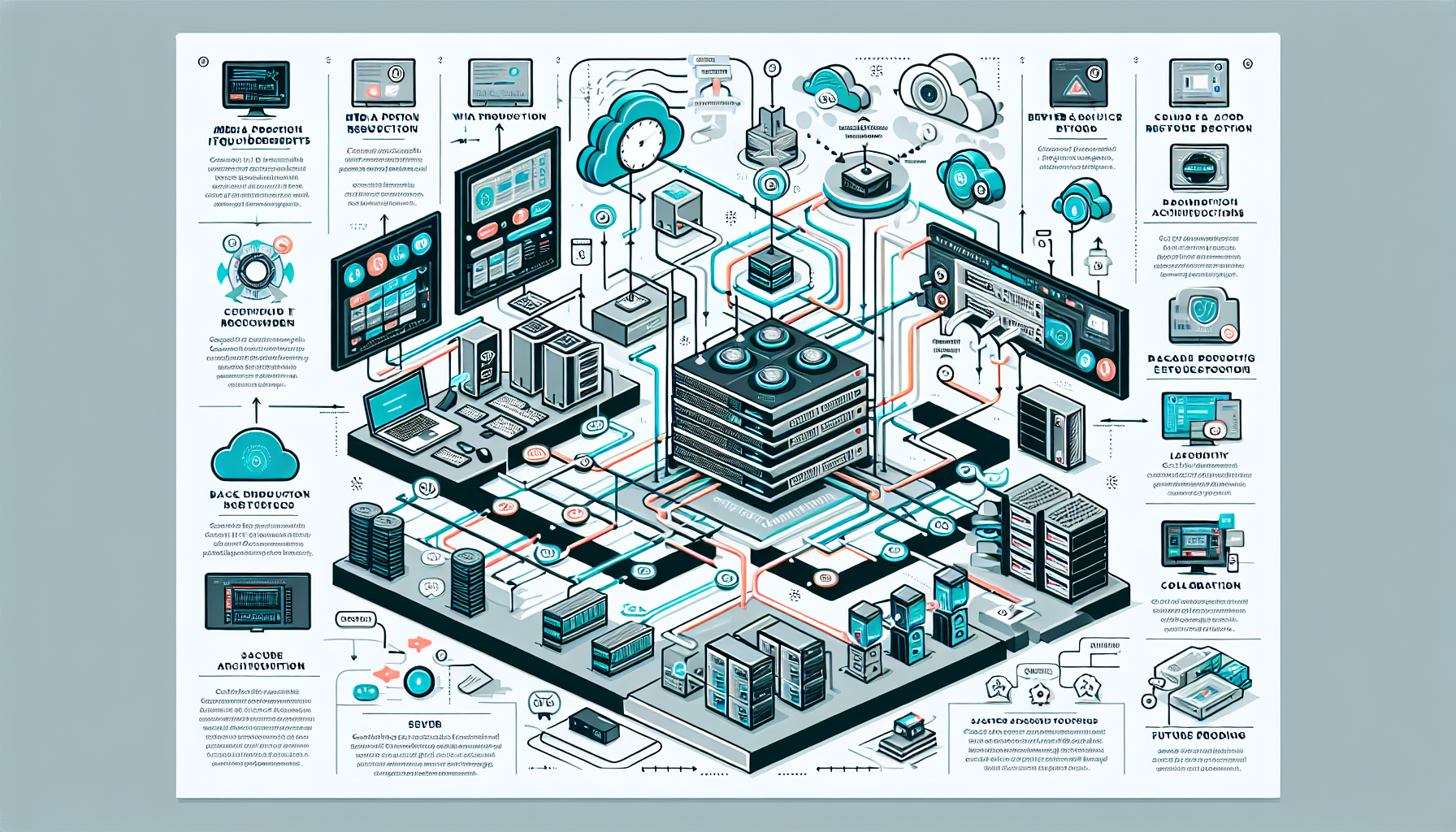
Configuring IT infrastructure for media production workflows involves designing a scalable, high-performance, and reliable system to support the demanding requirements of video editing, rendering, post-production, asset management, and collaboration. Below is a step-by-step guide for configuring your IT infrastructure:
1. Assess Media Production Requirements
- Understand Workflow Needs:
- File types (e.g., 4K, 8K, RAW, ProRes, etc.).
- File sizes and bandwidth requirements.
- Editing and rendering software (e.g., Adobe Premiere, Final Cut Pro, DaVinci Resolve, etc.).
- Collaboration requirements (on-premises vs remote).
- Performance Metrics:
- High throughput for large file transfers.
- Low latency for real-time editing.
- GPU acceleration for rendering and AI workflows.
2. Storage Architecture
- Centralized Storage:
- Use high-performance shared storage systems, such as NAS (Network Attached Storage) or SAN (Storage Area Network), with SSD or NVMe drives for fast read/write performance.
- Implement tiered storage for balancing performance and cost (e.g., NVMe for active projects, HDDs for archival).
- File System:
- Use file systems optimized for media workflows, such as SMB, NFS, or specialized systems like StorNext or BeeGFS.
- Storage Capacity:
- Plan for high capacity, scalable storage to accommodate large media files.
- Implement data compression and deduplication where feasible.
- Redundancy and Backup:
- Use RAID configurations for fault tolerance (e.g., RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10).
- Backup media files regularly using solutions like Veeam, Rubrik, or cloud backups.
3. Networking
- High-Speed Connectivity:
- Deploy high-speed networking (10GbE, 25GbE, or even 100GbE for larger setups) to ensure smooth file transfers and real-time editing.
- Use enterprise-grade switches with QoS (Quality of Service) for traffic prioritization.
- Remote Access:
- Implement VPNs or private cloud solutions for remote collaboration.
- Consider WAN acceleration tools like Aspera or Signiant for large file transfers.
- Network Segmentation:
- Segregate media production traffic from general office traffic for better performance and security.
4. Servers and Workstations
- Editing Workstations:
- Equip workstations with high-end CPUs (e.g., Intel i9, Xeon, or AMD Ryzen Threadripper).
- Use GPUs optimized for media production (e.g., NVIDIA RTX A6000, A4000, or AMD Radeon Pro).
- Install 32GB to 128GB of RAM depending on project complexity.
- Rendering and Encoding Servers:
- Deploy GPU-powered servers for rendering tasks (e.g., NVIDIA A100 or RTX series GPUs).
- Use virtualization or containerization (e.g., VMware, Kubernetes) to allocate resources dynamically.
- AI Workloads:
- For AI-driven media tasks (e.g., color grading, upscaling, content tagging), ensure availability of Tensor Core GPUs and AI frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
5. Virtualization and Kubernetes
- Virtualization:
- Use VMware, Hyper-V, or KVM to virtualize critical applications (e.g., project management, asset management systems).
- Kubernetes:
- Deploy Kubernetes clusters to run containerized workloads, such as AI pipelines, rendering services, or transcoding jobs.
- Use persistent storage with Kubernetes for media files (e.g., Portworx, OpenEBS).
6. Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Backup Strategy:
- Use a 3-2-1 backup approach: 3 copies of data, 2 different storage mediums, and 1 offsite copy (e.g., cloud storage).
- Backup Software:
- Implement tools like Veeam, Cohesity, or Commvault to automate backups and ensure RTO/RPO requirements are met.
- Disaster Recovery:
- Establish a DR plan with replication of critical data to a secondary data center or cloud environment.
7. Collaboration Tools
- Media Asset Management (MAM):
- Deploy a MAM system (e.g., CatDV, Axle AI, or Adobe Team Projects) for centralized media organization and collaboration.
- Cloud Collaboration:
- Use cloud platforms like Frame.io or LucidLink for remote teams to review and edit projects in real-time.
8. Security
- Access Control:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) for storage and applications.
- Use MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) for sensitive systems.
- Data Encryption:
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- Endpoint Protection:
- Deploy antivirus and EDR solutions for workstations and servers.
- Audit and Monitoring:
- Use centralized monitoring tools like Splunk or ELK Stack to track system performance and detect anomalies.
9. Cloud Integration
- Hybrid Cloud:
- Use hybrid cloud solutions to offload non-critical workloads (e.g., rendering or backup) to cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Cloud Storage:
- Leverage object storage services like Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, or Google Cloud Storage for archiving and long-term retention.
- Cloud Rendering:
- Use cloud rendering services like AWS Thinkbox Deadline or Google Cloud Render Farm for burst rendering capacity.
10. Monitoring and Maintenance
- Performance Monitoring:
- Use tools like Nagios, PRTG, or SolarWinds to monitor network and server performance.
- Hardware Maintenance:
- Schedule regular firmware and driver updates for storage, GPUs, and network equipment.
- User Training:
- Train teams on using the infrastructure efficiently, including MAM systems and collaboration tools.
11. Scalability and Future Proofing
- Modular Design:
- Build systems with modularity in mind to allow seamless upgrades (e.g., adding more GPUs, storage, or network bandwidth).
- Emerging Technologies:
- Explore emerging technologies like AI-powered editing tools, 8K video workflows, and cloud-native solutions to stay ahead.
Example Architecture
- Editing Workstations: High-end PCs with NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPUs and 10GbE connectivity.
- Storage Backend: 500TB shared SAN with NVMe drives for active projects and HDDs for archives.
- Render Farm: GPU-powered servers with Kubernetes and NVIDIA GPUs for distributed rendering.
- Network: 25GbE backbone with redundant switches and VPN for remote access.
- Backup: Local NAS for daily backups and S3-compatible cloud storage for offsite backups.
- Collaboration Tools: Frame.io for review/approval and a MAM system for asset management.
This infrastructure ensures high performance, collaboration, and scalability tailored to media production workflows.
How do I configure IT infrastructure for media production workflows?