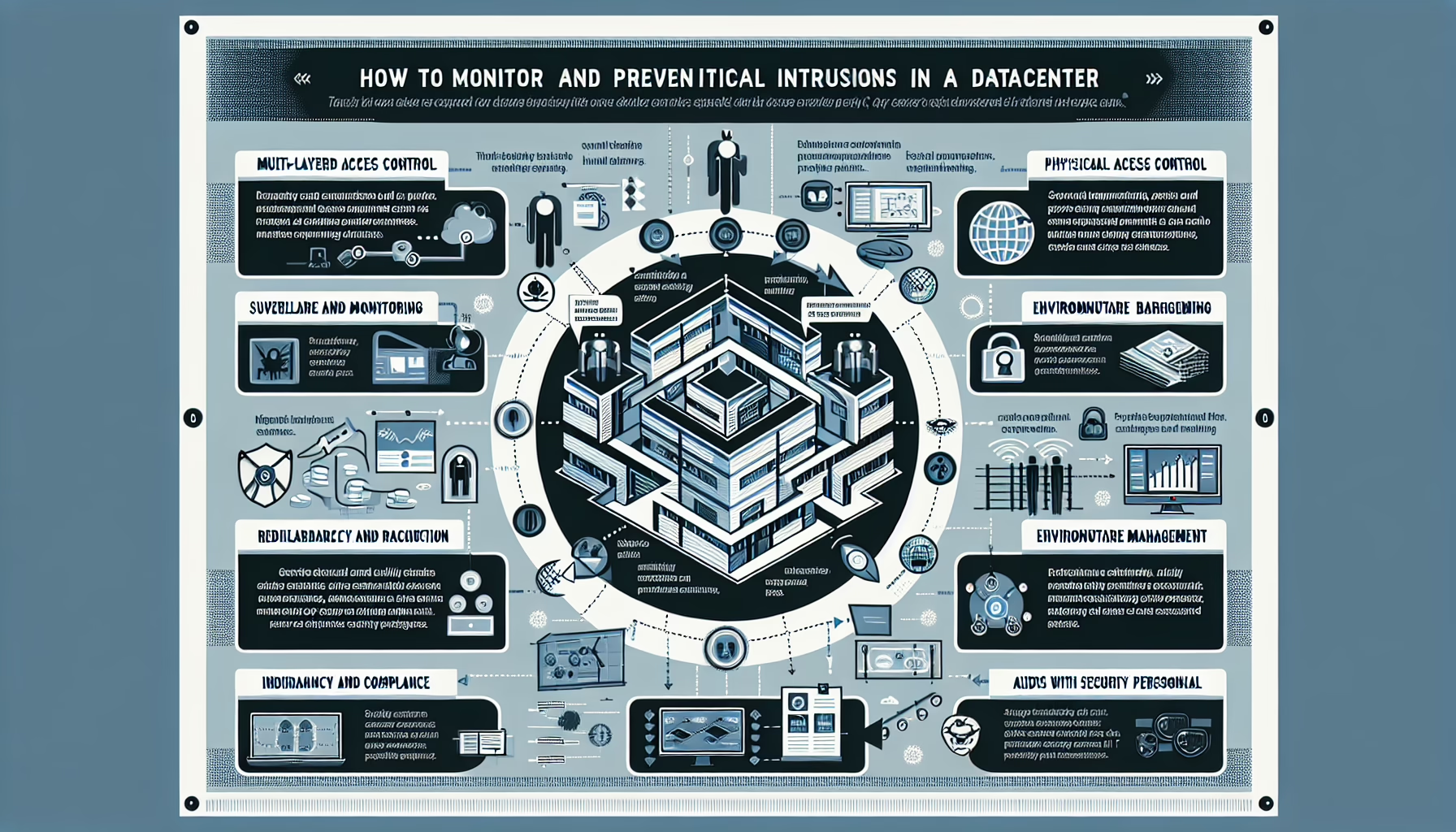
Monitoring and preventing physical intrusions in a datacenter is a critical aspect of securing your IT infrastructure. Here are several strategies and best practices to ensure your datacenter remains physically secure:
1. Implement Multi-Layered Access Control
- Perimeter Security: Install fences, gates, and barriers to restrict access to the datacenter premises. Use bollards to prevent vehicular access to sensitive areas.
- Access Card Systems: Use RFID cards, keycards, or biometric systems (fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scanners) to control access to the building and specific areas within the datacenter.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Combine physical access cards with PINs or biometric authentication for a stronger layer of security.
- Mantraps: Install mantraps (two sets of interlocking doors) where only one person can enter or exit at a time after verification.
2. Surveillance and Monitoring
- CCTV Cameras: Deploy high-definition cameras with night vision capabilities and a wide field of view to monitor all entry points, corridors, server rooms, and blind spots.
- Motion Detectors: Install motion sensors and integrate them with your surveillance system to trigger alerts for unauthorized movement.
- Monitoring Software: Use centralized monitoring software to view live feeds and review recordings. Integrate this with AI-powered anomaly detection systems to identify unusual behavior.
- Retention Policies: Maintain video footage for a specific retention period (e.g., 90 days) to aid investigations when needed.
3. Physical Barriers
- Secured Entry Points: Use reinforced doors with advanced locking mechanisms, such as electromagnetic locks, and ensure they are fire-rated.
- Rack-Level Security: Implement server rack locks and restrict access to individual racks to authorized personnel only.
- Secure Cabling: Use conduit or cable trays to protect network cables from tampering or accidental damage.
4. Visitor Management
- Pre-Registration: Require visitors to pre-register and verify their identity before entering the datacenter.
- Sign-In/Sign-Out Logs: Maintain detailed logs of all visitors and contractors, including their purpose of visit and areas accessed.
- Escort Policy: Ensure that visitors are always accompanied by authorized personnel.
- Temporary Access Badges: Issue access badges with limited permissions and expiration for temporary visitors.
5. Environmental Monitoring
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Install sensors on doors, windows, and walls to detect unauthorized entry or tampering.
- Vibration Sensors: Place vibration sensors on walls and floors to detect drilling or other forced entry attempts.
- Alarm Systems: Integrate alarms with intrusion detection systems to notify security personnel immediately in case of a breach.
6. Secure Policies and Procedures
- Background Checks: Conduct thorough background checks on employees, contractors, and vendors with access to the datacenter.
- Training: Train employees on physical security protocols, including recognizing tailgating (unauthorized individuals following authorized ones).
- Access Reviews: Regularly review access permissions to ensure only authorized personnel have access to sensitive areas.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a response plan for physical security breaches, including escalation procedures.
7. Redundancy and Fail-Safes
- Backup Power for Security Systems: Ensure surveillance cameras, access control systems, and alarms have backup power (UPS or generators) to remain operational during outages.
- Redundant Monitoring: Have security personnel monitor surveillance feeds in addition to automated systems to minimize missed incidents.
8. Audits and Compliance
- Physical Security Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify vulnerabilities in your physical security setup and address gaps promptly.
- Compliance Standards: Adhere to industry standards such as ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2, or PCI DSS, which often include physical security requirements.
- Penetration Testing: Hire physical security experts to perform penetration testing and identify weaknesses in your defenses.
9. Integration with IT Systems
- Access Logs Correlation: Integrate physical access logs with IT system logs to detect unusual patterns (e.g., someone accessing the datacenter at odd hours and performing unauthorized changes).
- IoT Sensors: Use Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to monitor environmental parameters like temperature, humidity, and unauthorized movements.
10. Employ On-Site Security Personnel
- 24/7 Security Staff: Deploy trained personnel to monitor entrances, exits, and critical areas.
- Regular Patrols: Conduct routine patrols within and around the datacenter to deter and detect intrusions.
- Emergency Response: Ensure security staff is equipped to respond to alarms or intrusions quickly.
By combining these measures, you can establish a robust physical security framework to monitor and prevent physical intrusions in your datacenter. It’s important to continuously evaluate and improve your security practices to address evolving threats.
How do I monitor and prevent physical intrusions in a datacenter?