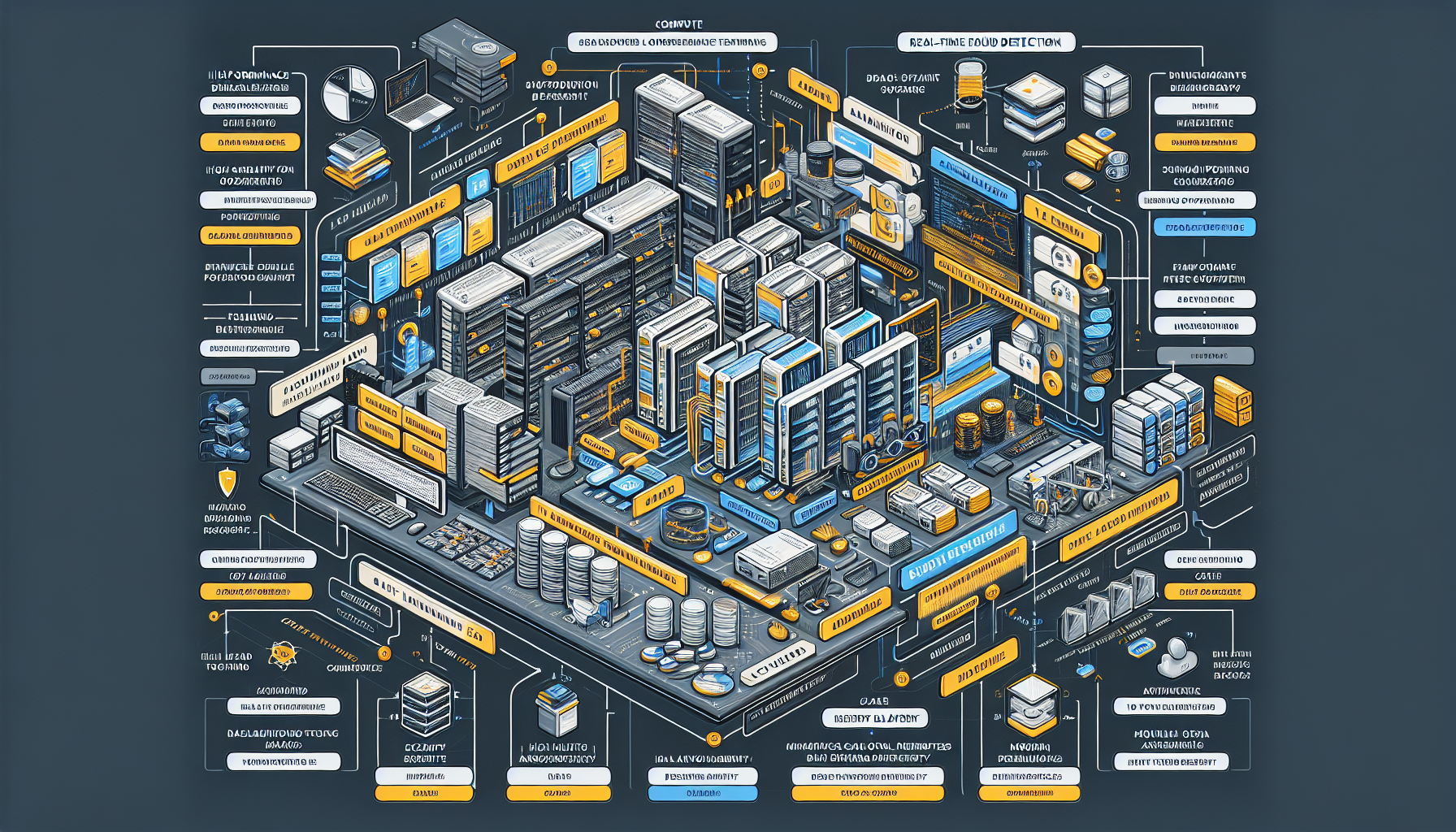
Configuring IT infrastructure for real-time fraud detection systems requires careful planning, design, and deployment to ensure high performance, scalability, reliability, and security. Fraud detection systems often rely on advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time data processing. Below is a step-by-step guide to building IT infrastructure for such systems:
1. Define Requirements
- Understand Fraud Detection Needs:
- Determine the types of fraud you’re detecting (e.g., financial, e-commerce, identity theft).
- Evaluate the volume, velocity, and variety of data to process.
- Performance Goals:
- Low latency for real-time detection.
- High throughput to handle large data streams.
- Availability and Reliability:
- Target high availability (e.g., 99.99%) and fault tolerance.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, PCI DSS, or CCPA.
2. Core IT Infrastructure Components
Compute
- High-Performance Servers:
- Use servers with multi-core CPUs and ample RAM for high-speed data processing.
- Leverage servers with GPUs for machine learning workloads.
-
Examples: NVIDIA A100 GPUs for model training and inference.
-
Scalability:
- Use virtualization or containerization to scale resources dynamically.
- Deploy Kubernetes clusters to orchestrate containerized fraud detection services.
Storage
- High-Speed Storage:
- Use NVMe SSDs for low-latency storage.
- Implement storage solutions optimized for big data analytics (e.g., Dell PowerStore, NetApp AFF systems).
- Object Storage for Data Lakes:
- Store historical data for training machine learning models.
- Examples: AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, or on-prem Ceph.
- Data Retention and Compliance:
- Implement storage tiering for warm and cold data to manage cost efficiently.
Networking
- Low-Latency Networks:
- Deploy high-speed networking (e.g., 10/25/100 Gbps Ethernet).
- Use software-defined networking (SDN) for traffic optimization.
- Edge Processing:
- Consider edge computing to process data closer to the source for faster fraud detection.
Databases
- Real-Time Databases:
- Use in-memory databases like Redis or Memcached for ultra-fast lookups.
- Deploy NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra for unstructured data.
- Event Streaming:
- Use Kafka or Apache Pulsar for real-time data ingestion and processing.
3. AI and Machine Learning Infrastructure
- Model Training:
- Use GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA A100, V100) for training fraud detection models.
- Leverage distributed ML frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Horovod.
- Model Inference:
- Deploy trained models on inference-optimized systems (e.g., NVIDIA Triton Inference Server).
- Use ONNX Runtime for optimized model execution.
- ML Operations (MLOps):
- Automate workflows for model training, deployment, and monitoring using tools like Kubeflow or MLflow.
- Pre-Built AI Services:
- Consider using cloud-based AI services like AWS Fraud Detector or Azure Machine Learning for rapid prototyping.
4. Real-Time Data Processing Framework
- Stream Processing:
- Use frameworks like Apache Flink, Apache Spark Streaming, or Apache Storm for processing data streams in real-time.
- Message Queues:
- Implement message brokers like RabbitMQ or Kafka to handle high-throughput data streams.
- Event-Driven Architecture:
- Build microservices that respond to events (e.g., suspicious transactions) in real-time.
5. Security and Compliance
- Data Encryption:
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit using TLS and AES-256.
- Access Control:
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Integrate with an identity provider (e.g., Okta, Azure AD).
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems:
- Deploy IDS/IPS to monitor and block suspicious activities.
- Auditing and Logging:
- Implement centralized logging with ELK Stack or Splunk for traceability and compliance.
6. High Availability and Disaster Recovery
- Redundancy:
- Deploy redundant servers, network connections, and storage systems.
- Load Balancing:
- Use load balancers (e.g., HAProxy, NGINX) to distribute traffic across servers.
- Backup and Recovery:
- Implement continuous data backup with solutions like Veeam or Rubrik.
- Test disaster recovery plans regularly.
7. Monitoring and Analytics
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- Use tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Datadog to monitor system performance.
- Set up alerts for anomalies or resource over-utilization.
- Log Analysis:
- Aggregate logs using ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Splunk.
- Performance Tuning:
- Continuously optimize database queries, model inference, and application code for better performance.
8. Cloud vs On-Premises
- Cloud:
- Use cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) for scalability and managed services.
- Examples: AWS Fraud Detector, BigQuery for analytics, or Azure Synapse.
- On-Premises:
- Use on-prem infrastructure for sensitive data or strict compliance requirements.
- Consider hybrid architectures for flexibility.
9. Testing and Validation
- Simulate Real-World Scenarios:
- Test the fraud detection system with realistic workloads and data.
- Stress Testing:
- Ensure the infrastructure can handle peak loads and failover scenarios.
- Latency Testing:
- Measure end-to-end latency to meet real-time requirements.
10. Continuous Improvement
- Feedback Loop:
- Continuously gather feedback from fraud detection outcomes to improve models and system performance.
- Regular Updates:
- Keep the infrastructure updated with the latest hardware, software, and security patches.
By setting up a robust, scalable, and secure IT infrastructure, you can ensure that your real-time fraud detection system operates efficiently and effectively, minimizing fraud risks while maintaining user trust.