Creating a reliable backup strategy is critical to ensure data integrity, availability, and disaster recovery in your IT environment. As an IT manager responsible for datacenters, storage, backup, and infrastructure, here’s a step-by-step guide to designing a robust backup strategy:
1. Define Objectives and Requirements
- Identify Critical Data: Determine which systems, applications, and data are mission-critical and need to be backed up.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): How quickly you need the data restored after a failure.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): How much data loss is acceptable (e.g., last 15 minutes, last hour, last day).
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Understand any regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOX) that may affect your backup strategy.
2. Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
The 3-2-1 rule is widely regarded as a best practice:
– 3 Copies of Data: Keep three copies of your data (production data + two backups).
– 2 Different Media: Store backups on at least two different types of media (e.g., disk, tape, cloud).
– 1 Offsite Copy: Keep one backup copy offsite for disaster recovery.
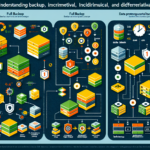
3. Choose Backup Types
Select the appropriate backup types based on your workload:
– Full Backup: A complete copy of all data. Best for periodic backups but time-consuming and storage-intensive.
– Incremental Backup: Backs up only the data that changed since the last backup (faster and efficient).
– Differential Backup: Backs up changes since the last full backup (a middle ground between full and incremental).
– Image-based Backup: Captures the entire system (OS, files, applications) as a snapshot for bare-metal recovery.
– Application-aware Backup: For databases, VMs, or Kubernetes pods, ensure backups are consistent by quiescing applications during backup.
4. Select Backup Tools and Platforms
- On-premises Backup:
- Use enterprise solutions like Veeam, Commvault, or Dell EMC Avamar for virtual machines and physical servers.
- Use Linux tools like
rsyncfor file-level backups or Bacula for centralized backups. - Cloud Backup:
- Use cloud-native tools like AWS Backup, Azure Backup, or Google Cloud Storage.
- Third-party multi-cloud tools like Rubrik or Druva can simplify hybrid cloud environments.
- Kubernetes Backup:
- Use tools like Velero, Kasten K10, or Trilio for containerized workloads.
- AI/High-Performance Workloads:
- Ensure GPU-based workloads are paused or checkpointed before backups. Use tools that support large data volumes and GPU nodes.
5. Automate and Schedule Backups
- Use automation to ensure backups run consistently:
- Schedule backups during off-peak hours to minimize performance impact.
- Use orchestration tools like Ansible or PowerShell scripts for custom backup workflows.
- For Kubernetes, schedule backups using CronJobs or native backup tools with scheduling capabilities.
6. Test Backup and Restore Regularly
- Simulate Recovery Scenarios: Perform regular test restores to verify backup integrity and ensure you can meet your RTO/RPO.
- Validate Consistency: Ensure databases, virtual machines, and files are restored without corruption.
- Document Procedures: Have clear disaster recovery (DR) and restore procedures accessible to the team.
7. Secure Your Backups
- Encryption: Encrypt backups both in-transit and at rest to prevent data breaches.
- Access Control: Restrict access to backup systems with role-based access control (RBAC).
- Immutable Backups: Use immutable storage (e.g., WORM) or object lock to protect backups from ransomware.
- Air-Gapped Backups: Isolate critical backups from the network to protect against cyberattacks.
8. Monitor and Optimize
- Backup Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track backup success/failure rates (e.g., Veeam ONE, Datadog, or SolarWinds).
- Storage Management: Monitor storage utilization and implement data deduplication and compression to optimize usage.
- Retention Policies: Define how long backups are retained (e.g., 7 days for incremental, 30 days for full, 1 year for archives).
9. Plan for Disaster Recovery
- Develop a disaster recovery plan that integrates with your backup strategy.
- Ensure offsite backups or cloud backups are easily accessible for emergencies.
- Use DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service) for critical workloads that require near-instant failover.
10. Document Your Backup Strategy
- Create detailed documentation covering:
- Backup schedules, tools, and locations.
- RTO/RPO goals and how they are achieved.
- Instructions for restoring data, testing, and troubleshooting.
- Contact information for team members and vendors.
11. Consider Modern Backup Trends
- Snapshot-based Backups: Use storage array snapshots (e.g., NetApp, Pure Storage) for faster backups and restores.
- Backup for AI Workloads: Ensure you back up large datasets, models, and GPU configurations critical for AI/ML pipelines.
- Hybrid Cloud Backup: Leverage both on-premises and cloud backups for flexibility and redundancy.
- Immutable Backups for Ransomware Protection: Use tools like AWS S3 Object Lock or Veeam Hardened Repository.
12. Budget and Evaluate ROI
- Factor in costs for hardware, software, cloud storage, bandwidth, and personnel.
- Evaluate ROI by considering potential downtime, data loss, and compliance penalties prevented by a robust backup strategy.
By following these steps, you can create a reliable, scalable, and secure backup strategy tailored to your IT environment. Regularly review and update the strategy to adapt to changing business needs, technologies, and threats.