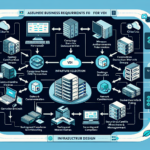
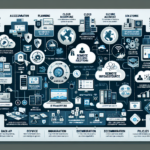
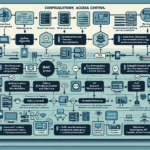
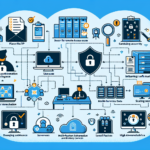
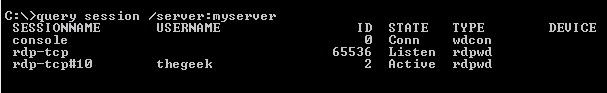Configuring IT infrastructure for remote desktop environments involves careful planning and implementation to ensure security, scalability, and performance for users accessing resources remotely. Below is a comprehensive guide for setting up IT infrastructure for a remote desktop environment:
1. Assess Requirements
- Determine User Needs: Understand the number of users, workloads (e.g., basic office apps, graphic-intensive tasks), and applications they need access to.
- Evaluate Performance Requirements: Consider CPU, GPU, memory, storage, and network bandwidth needed for smooth operation.
- Security Requirements: Define data protection, access control, and compliance needs.
2. Choose a Remote Desktop Solution
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS): Suitable for Windows-based environments.
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Solutions like VMware Horizon, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, or Azure Virtual Desktop for scalable deployments.
- Cloud-based Remote Desktops: AWS WorkSpaces or Google Cloud virtual desktops for cloud-native environments.
- Open Source Options: Solutions like Apache Guacamole for Linux-based environments.
3. Provision Server Infrastructure
- On-premises or Cloud: Decide whether to host the environment on-premises or leverage cloud services.
- Hardware Requirements:
- Servers: Deploy high-performance servers with sufficient CPU, RAM, and storage.
- GPU Cards: Use GPU-enabled servers (e.g., NVIDIA Tesla or A100) if users need access to graphic-intensive applications.
- Storage: Implement high-speed storage solutions (e.g., NVMe or SSD) for fast data access.
- Network: Ensure robust connectivity (gigabit or 10G networking) to handle remote traffic.
4. Virtualization Setup
- Hypervisor: Install and configure a virtualization platform like VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, or KVM.
- VM Provisioning: Create virtual machines (VMs) tailored for users or groups of users.
- Scalability: Use automation tools to scale VMs dynamically based on load and demand.
5. Configure Remote Access
- Network Configuration:
- Implement VPN solutions for secure remote connections.
- Enable RDP or other protocols (e.g., ICA, PCoIP) for remote access.
- Ensure proper firewall rules and NAT configurations.
- Security:
- Configure multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user access.
- Use encrypted protocols (e.g., TLS 1.2+) for secure data transmission.
- Regularly patch and update all software and OS.
6. Storage and Backup
- Centralized Storage:
- Use SAN/NAS systems or cloud storage for shared user data.
- Implement high-performance storage to reduce latency for users.
- Backup Solution:
- Set up automated backups for user data and configurations using tools like Veeam, Commvault, or native solutions.
- Store backups in geographically diverse locations for disaster recovery.
7. Implement Kubernetes and AI Integration (Optional)
- If the remote desktop environment is used for advanced workloads like AI/ML:
- Kubernetes: Deploy Kubernetes clusters to orchestrate GPU workloads and containerized applications.
- AI Frameworks: Optimize infrastructure for TensorFlow, PyTorch, or other AI tools. Leverage GPU cards like NVIDIA A100 for AI workloads.
- Storage: Use high-speed storage like Ceph or NVMe for faster data access during AI processing.
8. User Profile Management
- Profile Configuration: Use roaming profiles or FSLogix to ensure consistent user experience across sessions.
- Group Policies: Configure appropriate Windows Group Policies for application access, security, and resource allocation.
9. Monitoring and Optimization
- Performance Monitoring:
- Use tools like SolarWinds, PRTG, or native hypervisor/cloud monitoring tools.
- Monitor CPU, RAM, disk I/O, and network traffic for bottlenecks.
- Capacity Planning: Regularly review usage trends to scale infrastructure ahead of demand.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from users to identify areas for improvement.
10. Disaster Recovery and Failover
- Redundancy: Deploy failover systems (e.g., clustered servers or cloud-based replicas).
- Recovery Plan: Ensure backups and snapshots are available to quickly recover user environments in case of failure.
11. Test the Environment
- Pilot Testing: Test the remote desktop setup with a small group of users to identify issues.
- Load Testing: Simulate high user traffic to ensure the infrastructure can handle peak loads.
12. Documentation and Training
- Document Configuration: Maintain detailed documentation of your setup, including server specs, IP addresses, and configurations.
- User Training: Train users on how to securely access the remote desktop environment and use applications effectively.
13. Continuous Improvement
- Regularly update software and hardware to keep the environment secure and performant.
- Review usage reports and optimize resource allocation as needed.
By following these steps, you can build a reliable and secure IT infrastructure for remote desktop environments tailored to your organization’s needs.
How do I configure IT infrastructure for remote desktop environments?