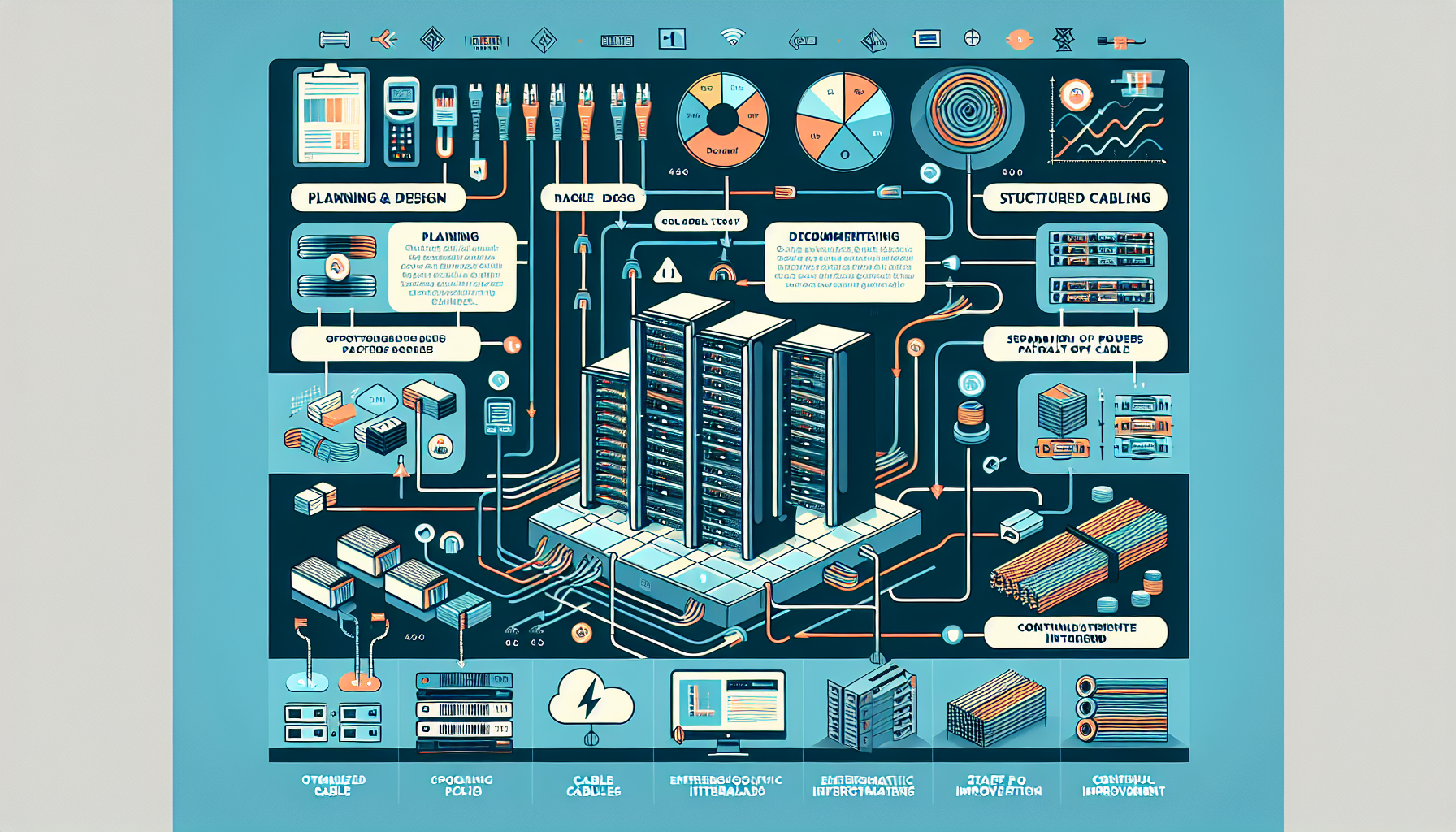
Effective cable management is a critical aspect of maintaining a well-organized, efficient, and reliable data center. Proper cable management not only ensures system reliability and performance but also facilitates maintenance, scalability, and safety. Here are the best practices for cable management in data centers:
1. Plan and Design Before Deployment
- Document Everything: Create detailed network and cabling diagrams to map out all connections, pathways, and equipment placements.
- Standardize Cabling: Use a consistent color-coding scheme and labeling system for cables to differentiate between network types, power cables, and other connections (e.g., blue for Ethernet, red for power, etc.).
- Allow for Growth: Design cabling pathways with extra capacity for future expansion to avoid overcrowding.
- Follow Industry Standards: Adhere to standards like TIA/EIA-568 and ISO/IEC 11801 for structured cabling to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
2. Use Structured Cabling
- Horizontal and Vertical Cable Management: Use cable trays, ladder racks, or raceways for horizontal cable runs, and vertical managers for rack-mounted equipment.
- Minimize Cable Length: Avoid unnecessarily long cables to reduce clutter, improve airflow, and minimize signal degradation.
- Patch Panels: Utilize patch panels for terminating and organizing cables. This simplifies maintenance and reduces wear on server and switch ports.
- Pre-Terminated Cables: Use pre-terminated cables when possible to reduce installation time and errors.
3. Label and Document Cables
- Label Both Ends: Clearly label both ends of each cable to avoid confusion during troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep an updated record of all cable connections, including their purpose, source, and destination.
4. Separate Power and Data Cables
- Avoid Interference: Route power and data cables separately to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Use Shielded Cables: Where EMI is a concern, use shielded cables for data transmission.
5. Optimize Rack Design
- Cable Entry and Exit Points: Use grommets or cable ports to guide cables neatly into and out of racks.
- Cable Management Accessories: Install cable management bars, arms, or Velcro ties within racks to keep cables organized and prevent tangling.
- Leave Slack for Maintenance: Leave a small amount of slack to allow flexibility for maintenance without excessive cable loops.
6. Prioritize Cooling and Airflow
- Avoid Blocking Airflow: Ensure cables do not obstruct airflow to or from equipment, as this can lead to overheating.
- Use Raised Floors or Overhead Pathways: Implement either raised floors or overhead cable trays to keep cables off the ground and out of critical airflow paths.
7. Utilize High-Quality Materials
- Durable Cables: Use high-quality cables that meet or exceed performance standards to ensure reliability.
- Cable Ties: Use Velcro ties instead of plastic zip ties to avoid damaging cables and facilitate easy adjustments.
8. Perform Regular Maintenance
- Audit Cables Periodically: Periodically check cables for wear, damage, or unnecessary runs and replace or remove them as needed.
- Keep Cables Tidy: Regularly re-secure loose cables and address any new tangles or clutter.
- Remove Unused Cables: Decommission and remove old or unused cables to reduce congestion.
9. Train Staff and Enforce Policies
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce clear SOPs for cable management and handling.
- Training: Train technicians and staff on proper cabling techniques and standards to maintain consistency.
10. Invest in Monitoring and Smart Cable Management
- Cable Management Tools: Use intelligent cable management solutions that track cable connections and provide alerts for disconnected or misconfigured cables.
- Environmental Monitoring: Implement sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure that cable runs do not compromise the data center environment.
11. Color Coding and Categorization
- Color Coding: Use different colors for specific cable types (e.g., Ethernet, fiber optics, power) to make identification easier.
- Bundle Similar Cables: Group cables by function or destination to streamline maintenance and troubleshooting.
12. Use Fiber Optics Where Applicable
- High-Density Cabling: Fiber optics allow for higher data transfer rates and reduce cable bulk, which can improve cable management significantly.
- Protect Fiber Cables: Ensure proper protection for fragile fiber optic cables to avoid damage during handling.
13. Monitor and Improve Continuously
- Feedback Loop: Regularly review the effectiveness of your cable management and make iterative improvements.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with industry trends and new cable management technologies.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your data center operates efficiently with minimal downtime, easier troubleshooting, and scalability for future growth.