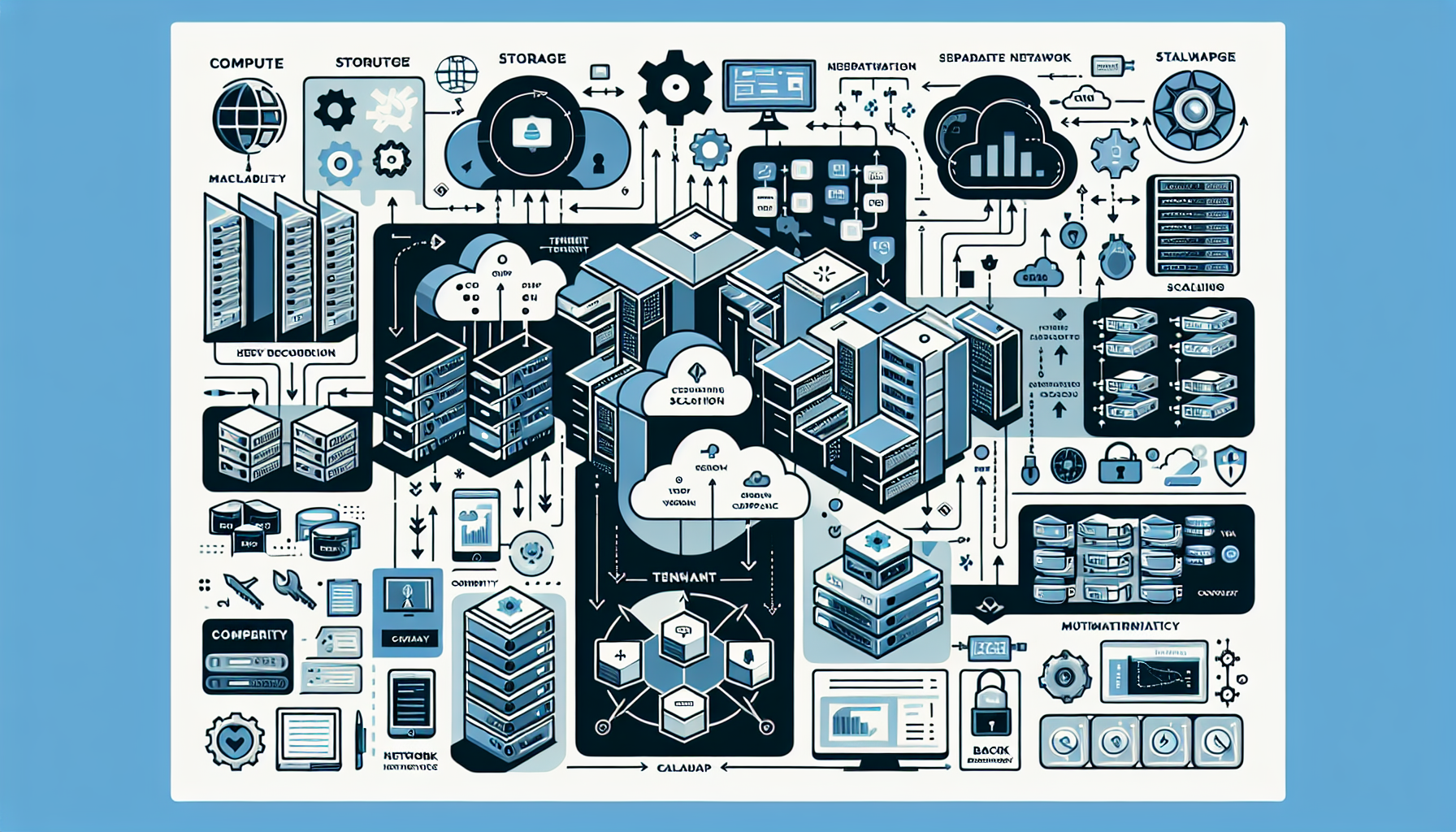
Configuring IT infrastructure for multi-tenant environments requires careful planning and execution to ensure isolation, performance, security, and scalability for multiple tenants. A multi-tenant architecture allows multiple customers (tenants) to share the same infrastructure resources while maintaining logical separation. Below is a step-by-step guide to designing and configuring IT infrastructure for multi-tenancy:
1. Understand Tenant Requirements
- Gather tenant-specific needs such as compute, storage, network, security, and compliance.
- Define Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for performance, uptime, and support.
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
2. Choose the Right Infrastructure Technology
- Virtualization: Use hypervisors (VMware, Hyper-V, KVM) to create isolated virtual machines (VMs) for each tenant.
- Containers: Use Kubernetes (K8s) to orchestrate containerized environments for lightweight isolation.
- Bare-Metal: For tenants requiring high performance or special hardware (e.g., GPU), use bare-metal servers and leverage tenant-specific isolation.
- Cloud Platforms: Public cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud offer multi-tenancy features.
3. Networking Configuration
- Virtual Networks (VNets): Create separate virtual networks for each tenant to isolate their traffic.
- VLANs: Use VLANs to segment tenant traffic on physical networks.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Implement SDN solutions (e.g., VMware NSX, Cisco ACI) to manage and automate tenant network configurations.
- Firewalls: Deploy tenant-specific firewall rules to prevent cross-tenant access.
- Load Balancers: Use tenant-aware load balancers to ensure fair resource distribution and high availability.
4. Storage Configuration
- Logical Volume Management (LVM): Use LVM to allocate separate storage volumes for each tenant.
- Storage Protocols: Leverage NFS, iSCSI, or object storage solutions for scalable tenant storage.
- Quotas: Enforce storage quotas to prevent one tenant from consuming excessive resources.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to ensure tenant data security.
5. Compute Resource Allocation
- Resource Pools: Use hypervisor resource pools to allocate and limit CPU, memory, and GPU resources for tenants.
- GPU Partitioning: For AI/ML workloads, consider GPU virtualization (e.g., NVIDIA vGPU) to share GPU resources across tenants.
- Scaling: Implement horizontal and vertical scaling options to meet tenant demands dynamically.
6. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Implement tenant-specific user directories or integrate with existing IAM solutions (e.g., Azure AD, Okta).
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit tenant administrators and users to their own environments.
- Enable single sign-on (SSO) for a seamless experience.
7. Security
- Isolation: Ensure complete isolation of tenant environments to prevent data leakage or unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encrypt tenant data using strong encryption algorithms (e.g., AES-256).
- Monitoring: Deploy security monitoring tools (e.g., SIEM) to detect and respond to suspicious activity.
- Auditing: Enable logging and auditing for tenant-specific actions to meet compliance standards.
8. Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Configure tenant-specific backup policies using tools like Veeam, Commvault, or NetBackup.
- Ensure backups are encrypted and stored in isolated repositories.
- Implement disaster recovery plans, including failover mechanisms, for tenant environments.
9. Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- Use monitoring tools (e.g., Prometheus, Nagios, SolarWinds) to track tenant resource usage.
- Set up alerts for resource over-utilization or under-utilization.
- Optimize resource allocation using automation tools and policies.
10. Automation and Orchestration
- Use Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or Ansible to deploy tenant environments quickly.
- Automate provisioning, scaling, and decommissioning of tenant resources to reduce manual effort.
- Employ Kubernetes Operators or Helm charts for multi-tenant containerized environments.
11. Billing and Cost Management
- Implement chargeback or showback models to track tenant resource usage and costs.
- Use tools like VMware vRealize Operations, AWS Cost Explorer, or Azure Cost Management for billing and reporting.
12. Compliance
- Isolate tenant environments to meet data residency and compliance requirements.
- Regularly audit tenant environments for compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, etc.
Tools and Technologies to Consider:
- Virtualization: VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, Proxmox.
- Containers: Kubernetes, Docker, Red Hat OpenShift.
- Storage: NetApp, Dell EMC, AWS S3.
- Networking: Cisco ACI, VMware NSX, Juniper Contrail.
- Backup: Veeam, Rubrik, Cohesity.
- Monitoring: Grafana, Prometheus, Datadog.
- Security: Palo Alto, Fortinet, CrowdStrike.
By following these principles and leveraging the appropriate tools, you can design and manage a robust multi-tenant IT infrastructure that meets the needs of your tenants while maintaining security, scalability, and operational efficiency.

Ali YAZICI is a Senior IT Infrastructure Manager with 15+ years of enterprise experience. While a recognized expert in datacenter architecture, multi-cloud environments, storage, and advanced data protection and Commvault automation , his current focus is on next-generation datacenter technologies, including NVIDIA GPU architecture, high-performance server virtualization, and implementing AI-driven tools. He shares his practical, hands-on experience and combination of his personal field notes and “Expert-Driven AI.” he use AI tools as an assistant to structure drafts, which he then heavily edit, fact-check, and infuse with my own practical experience, original screenshots , and “in-the-trenches” insights that only a human expert can provide.
If you found this content valuable, [support this ad-free work with a coffee]. Connect with him on [LinkedIn].