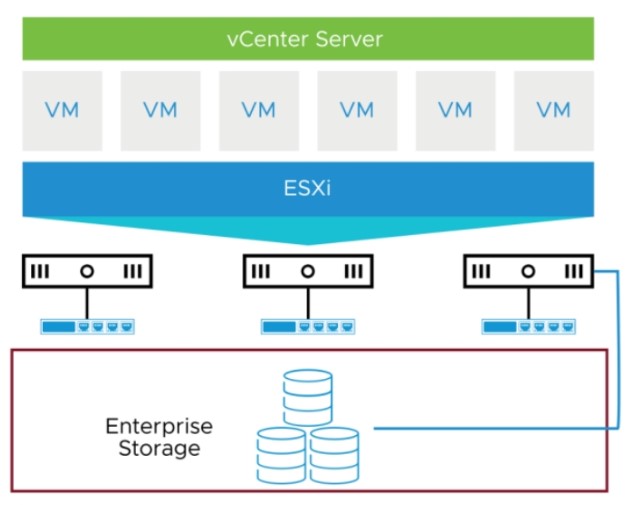
Configuring Active Directory (AD) Sites and Services for a multi-branch network is crucial to ensure efficient authentication, replication, and resource access. Below is a step-by-step guide to properly configure AD Sites and Services for a multi-branch network:
1. Understand Your Network Topology
Before configuring AD Sites and Services, gather the following information:
– Locations of each branch office.
– Subnet information for each branch.
– Network bandwidth between branches.
– The number of Domain Controllers (DCs) and their locations.
– Replication schedule considerations for bandwidth-constrained links.
2. Access Active Directory Sites and Services
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services tool from the Administrative Tools menu on a Domain Controller or a management workstation.
- Ensure you have administrative privileges to make changes.
3. Create Sites for Each Branch
- Expand the Sites node.
- Right-click on Sites and select New Site.
- Name the site (e.g., “Branch1” or “NewYorkOffice”).
- Select a Default Site Link (you can create or modify site links later).
- Click OK to create the site.
4. Add Subnets to Sites
- Expand the new site you created.
- Right-click on Subnets and select New Subnet.
- Enter the subnet details for the branch office in CIDR notation (e.g.,
192.168.1.0/24). - Assign the subnet to the appropriate site.
- Click OK to save.
By associating subnets with sites, AD can direct users and computers to the nearest Domain Controller for authentication.
5. Move Domain Controllers to the Correct Sites
- Under Sites, expand the Default-First-Site-Name (or wherever the Domain Controller is currently located).
- Find your Domain Controller under Servers.
- Drag the Domain Controller to the new site you created for that branch.
- Ensure the NTDS Settings object under the Domain Controller is configured for replication.
6. Configure Site Links
Site links define how replication occurs between sites. By default, AD creates a single site link, but you may need to create additional links based on your network topology.
1. Expand the Inter-Site Transports node under Sites.
2. Right-click on IP and select New Site Link.
3. Add the sites that should be connected by this link.
4. Name the site link (e.g., “HQ-to-Branch1”).
5. Set a Cost value (lower cost = higher priority for replication).
6. Set a replication schedule (if necessary) to avoid saturating WAN links during business hours.
7. Optimize Replication
- Replication Cost: Assign higher costs to slower or less reliable links.
- Replication Schedule: Schedule replication during off-peak hours for bandwidth-constrained links.
- Bridgehead Servers: Ensure one or more Domain Controllers in each site are designated as bridgehead servers to handle inter-site replication.
8. Verify and Test Configuration
- Use the repadmin command to check replication status:
repadmin /showrepl - Use the dcdiag tool to verify Domain Controller health:
dcdiag /s:<DomainControllerName> - Test authentication by logging in from a client machine in each branch and ensuring it connects to the local Domain Controller.
9. Configure Global Catalog (Optional)
If users in the branch offices need quick access to resources across the entire forest, consider enabling the Global Catalog on Domain Controllers in those branches.
10. Monitor and Maintain
- Regularly check replication health using repadmin and event logs.
- Document your AD Sites and Services configuration for future reference.
- Update site and subnet information as your network grows or changes.
Best Practices
- Plan Ahead: Design your AD Sites and Services configuration before deploying.
- Minimize Replication Traffic: Use site links and schedules to reduce unnecessary replication traffic over WAN links.
- Disaster Recovery: Ensure each site has at least one Domain Controller to maintain local authentication during WAN outages.
- DNS Configuration: Ensure DNS servers are properly configured to reflect the changes in sites and services.
By following these steps, you can optimize Active Directory performance across a multi-branch network, improve authentication efficiency, and maintain a robust IT infrastructure.

Ali YAZICI is a Senior IT Infrastructure Manager with 15+ years of enterprise experience. While a recognized expert in datacenter architecture, multi-cloud environments, storage, and advanced data protection and Commvault automation , his current focus is on next-generation datacenter technologies, including NVIDIA GPU architecture, high-performance server virtualization, and implementing AI-driven tools. He shares his practical, hands-on experience and combination of his personal field notes and “Expert-Driven AI.” he use AI tools as an assistant to structure drafts, which he then heavily edit, fact-check, and infuse with my own practical experience, original screenshots , and “in-the-trenches” insights that only a human expert can provide.
If you found this content valuable, [support this ad-free work with a coffee]. Connect with him on [LinkedIn].