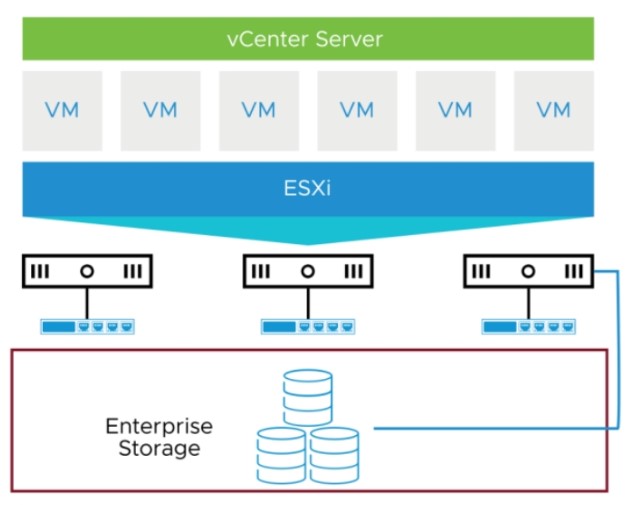
Configuring iSCSI multipathing is essential for fault tolerance and improved performance in your storage environment. Multipathing allows an iSCSI initiator to use multiple network paths to access storage targets, ensuring high availability and load balancing. Below is a step-by-step guide to configure iSCSI multipathing:
Prerequisites
- iSCSI Storage Array: Ensure your storage array supports multipathing.
- Multiple Network Interfaces: At least two network interfaces on the host and storage.
- Configured VLANs/Subnets: Ensure the storage and host are connected to separate VLANs/subnets for each path.
- iSCSI Software: Install the iSCSI initiator software on the host.
- Multipath Software: Install multipath software such as
Device Mapper Multipathon Linux orMPIOon Windows. - Ensure Connectivity: Verify network connectivity between the host and storage targets for all paths.
Steps for Linux Systems
1. Install Required Packages
Install the iSCSI initiator and multipath tools:
bash
sudo apt-get install open-iscsi multipath-tools
or
bash
sudo yum install iscsi-initiator-utils device-mapper-multipath
2. Configure iSCSI Initiator
Edit the iSCSI initiator configuration file (/etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi) and set the initiator name:
bash
InitiatorName=iqn.2023-01.com.example:host01
3. Discover iSCSI Targets
Discover the iSCSI targets using the iscsiadm command:
bash
sudo iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p <target_ip>
Repeat this command for each target IP.
4. Log In to Targets
Log in to the iSCSI targets:
bash
sudo iscsiadm -m node -T <target_name> -p <target_ip> --login
Repeat for each target path.
5. Enable Multipathing
Configure multipath:
– Edit /etc/multipath.conf:
text
defaults {
user_friendly_names yes
path_grouping_policy multibus
}
blacklist {
devnode "^sd[a-z]"
}
– Restart the multipath daemon:
bash
sudo systemctl restart multipathd
6. Verify Multipath Configuration
Check the multipath status:
bash
sudo multipath -ll
You should see multiple paths for the same storage device.
7. Configure Persistent Login
To ensure iSCSI sessions persist after reboot, enable the iSCSI service:
bash
sudo systemctl enable iscsid
sudo systemctl enable multipathd
Steps for Windows Systems
1. Install iSCSI Initiator
- Open the iSCSI Initiator in the Control Panel (
iscsicpl.exe). - Configure the iSCSI initiator name.
2. Discover and Connect to Targets
- Go to the
Discoverytab and add the IP addresses of the target storage. - Go to the
Targetstab, and connect to the discovered targets.
3. Install and Configure MPIO
- Install Multipath I/O (MPIO) feature:
- In Server Manager, go to
Add Roles and Features→ EnableMPIO. - Configure MPIO:
- Open
MPIO Propertiesfrom the Control Panel. - Add support for iSCSI devices under the
Discover Multi-Pathstab. - Restart the server.
4. Enable Multipath for iSCSI Targets
- Reconnect the iSCSI targets.
- Verify multipathing:
- Open
Disk Management. - Check if the disks have multiple paths.
5. Configure Load Balancing
Configure the load-balancing policy for MPIO:
– Open MPIO Properties.
– Set the Load Balancing Policy to Round Robin or Least Queue Depth for performance.
Best Practices
- Separate Networks: Use dedicated storage networks/VLANs for iSCSI traffic.
- Redundant Paths: Ensure redundant physical connections (NICs, switches) for fault tolerance.
- Jumbo Frames: Enable jumbo frames (MTU 9000) for improved performance.
- Network Bonding/Teaming: Consider NIC bonding or teaming for additional redundancy.
- Monitor Paths: Regularly monitor the multipath configuration for path failures.
Troubleshooting
- Check Connectivity:
- Use
pingortelnetto test connectivity to the storage IPs. - Verify Multipath Status:
- On Linux:
multipath -ll - On Windows: Check MPIO properties and path count.
- Logs:
- Linux:
/var/log/messagesor/var/log/syslog. - Windows: Event Viewer → Storage Logs.
By following these steps, you’ll have a robust iSCSI multipathing setup with enhanced fault tolerance and performance.

Ali YAZICI is a Senior IT Infrastructure Manager with 15+ years of enterprise experience. While a recognized expert in datacenter architecture, multi-cloud environments, storage, and advanced data protection and Commvault automation , his current focus is on next-generation datacenter technologies, including NVIDIA GPU architecture, high-performance server virtualization, and implementing AI-driven tools. He shares his practical, hands-on experience and combination of his personal field notes and “Expert-Driven AI.” he use AI tools as an assistant to structure drafts, which he then heavily edit, fact-check, and infuse with my own practical experience, original screenshots , and “in-the-trenches” insights that only a human expert can provide.
If you found this content valuable, [support this ad-free work with a coffee]. Connect with him on [LinkedIn].